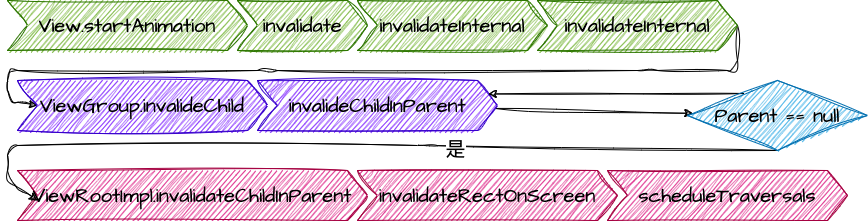
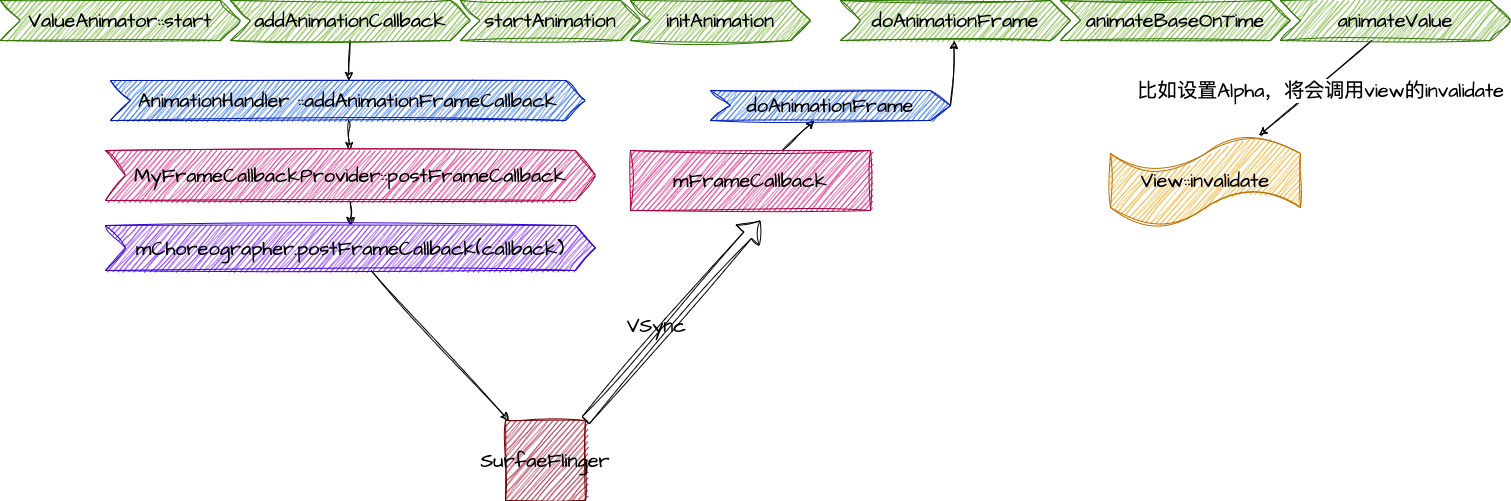
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
| public class View implements Drawable.Callback, KeyEvent.Callback,
AccessibilityEventSource {
//部分代码省略
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
/***部分代码省略***/
//如果有子 View(DecorView当然有子View),就会调用dispatchDraw() 将绘制事件通知给子 View。
//ViewGroup 重写了 dispatchDraw(),调用了 drawChild()
//drawChild() 调用了子 View 的 draw(Canvas, ViewGroup, long)
}
boolean draw(Canvas canvas, ViewGroup parent, long drawingTime) {
final boolean hardwareAcceleratedCanvas = canvas.isHardwareAccelerated();
/***部分代码省略***/
Transformation transformToApply = null;
boolean concatMatrix = false;
final boolean scalingRequired = mAttachInfo != null && mAttachInfo.mScalingRequired;
final Animation a = getAnimation();
if (a != null) {
more = applyLegacyAnimation(parent, drawingTime, a, scalingRequired);
concatMatrix = a.willChangeTransformationMatrix();
if (concatMatrix) {
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_VIEW_IS_ANIMATING_TRANSFORM;
}
transformToApply = parent.getChildTransformation();
} else {
/***部分代码省略***/
}
/***部分代码省略***/
// 动画数据应用在RenderNode或者Canvas上的!!!!
if (transformToApply != null) {
if (concatMatrix) {
if (drawingWithRenderNode) {
// 应用动画数据
renderNode.setAnimationMatrix(transformToApply.getMatrix());
} else {
canvas.translate(-transX, -transY);
// 应用动画数据
canvas.concat(transformToApply.getMatrix());
canvas.translate(transX, transY);
}
parent.mGroupFlags |= ViewGroup.FLAG_CLEAR_TRANSFORMATION;
}
float transformAlpha = transformToApply.getAlpha();
if (transformAlpha < 1) {
// 应用动画数据
alpha *= transformAlpha;
parent.mGroupFlags |= ViewGroup.FLAG_CLEAR_TRANSFORMATION;
}
}
}
private boolean applyLegacyAnimation(ViewGroup parent, long drawingTime,
Animation a, boolean scalingRequired) {
/***部分代码省略***/
//绘制动画的当前帧,并获取当前动画的状态(是否继续运行)
boolean more = a.getTransformation(drawingTime, t, 1f);
if (scalingRequired && mAttachInfo.mApplicationScale != 1f) {
if (parent.mInvalidationTransformation == null) {
parent.mInvalidationTransformation = new Transformation();
}
invalidationTransform = parent.mInvalidationTransformation;
a.getTransformation(drawingTime, invalidationTransform, 1f);
} else {
invalidationTransform = t;
}
//如果动画没有结果
if (more) {
if (!a.willChangeBounds()) {
if ((flags & (ViewGroup.FLAG_OPTIMIZE_INVALIDATE | ViewGroup.FLAG_ANIMATION_DONE)) ==
ViewGroup.FLAG_OPTIMIZE_INVALIDATE) {
parent.mGroupFlags |= ViewGroup.FLAG_INVALIDATE_REQUIRED;
} else if ((flags & ViewGroup.FLAG_INVALIDATE_REQUIRED) == 0) {
// The child need to draw an animation, potentially offscreen, so
// make sure we do not cancel invalidate requests
parent.mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAW_ANIMATION;
//进行绘制
parent.invalidate(mLeft, mTop, mRight, mBottom);
}
} else {
/***部分代码省略***/
//进行绘制
parent.invalidate(left, top, left + (int) (region.width() + .5f),
top + (int) (region.height() + .5f));
}
}
return more;
}
}
|
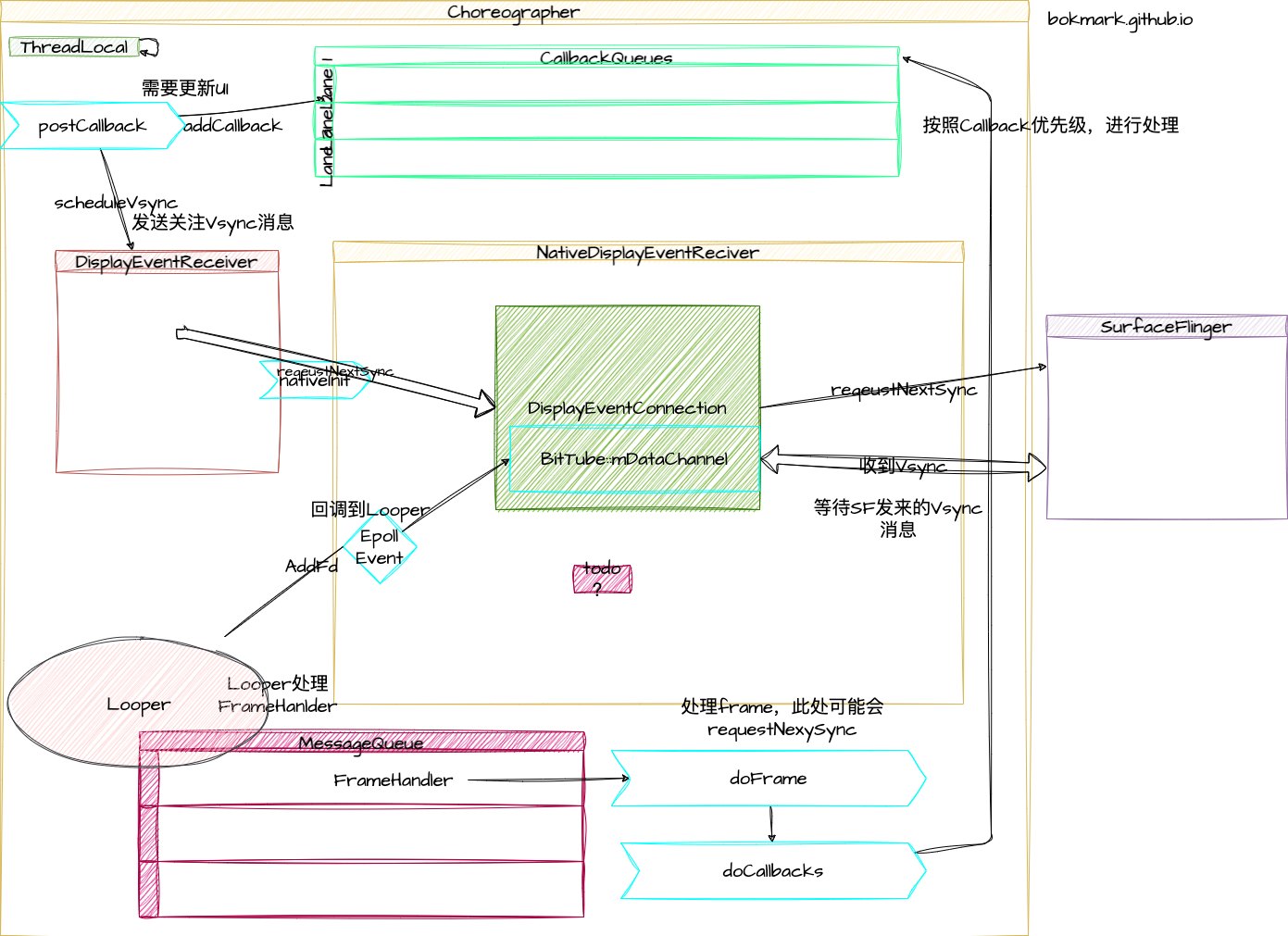
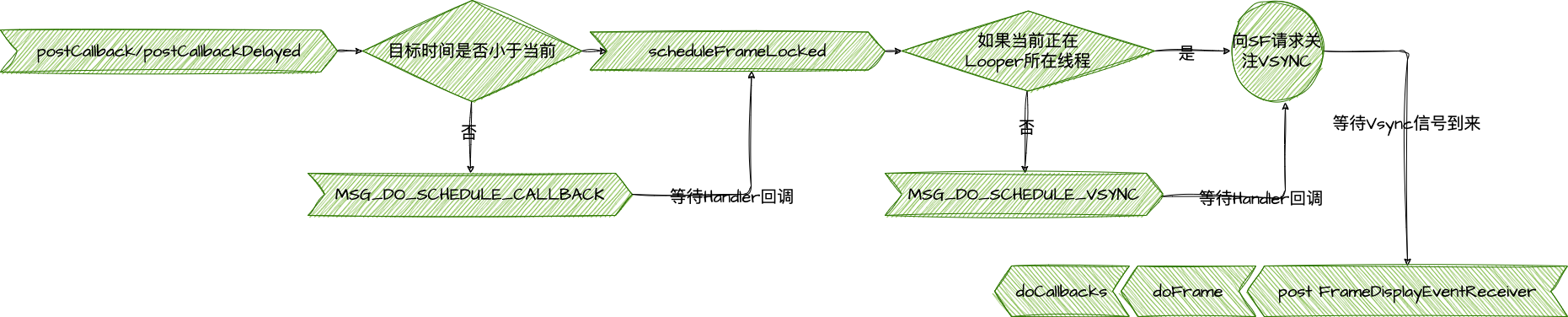
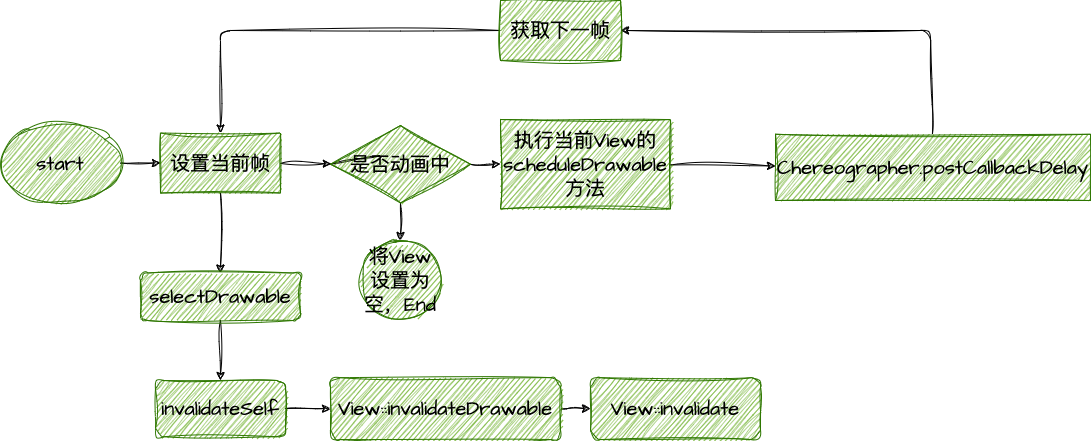 主要类为 AnimationDrawable。
主要类为 AnimationDrawable。